Designing for zero gravity is one thing – writing about it without sounding like a flight manual? That might just be trickier.
This guide will help you build a CV that’s not just technically impressive, but also strategically written. With clear advice and 2 Aerospace Engineering CV examples, you’ll learn how to elevate your application and glide into interviews.
Aerospace Engineering CV
Aeronautical Engineer CV

How to write your Aerospace Engineering CV
Discover how to craft a winning Aerospace Engineering CV that lands interviews with this simple step-by-step guide.
Aerospace engineering isn’t just about calculations and CAD models – it’s about solving real-world problems in high-stakes environments. Whether you specialise in aerodynamics, propulsion, or structures, your CV needs to showcase how you’ve applied technical knowledge in meaningful ways.
This guide walks through everything from formatting to content, helping you with writing a CV that communicates your capabilities with the same precision you apply to your designs.
The correct structure and formatting for an Aerospace Engineering CV
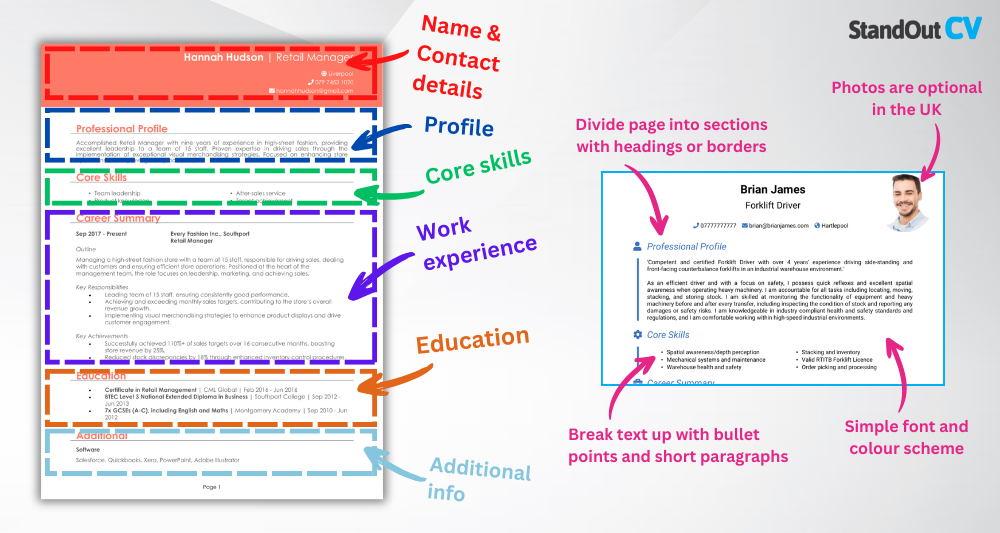
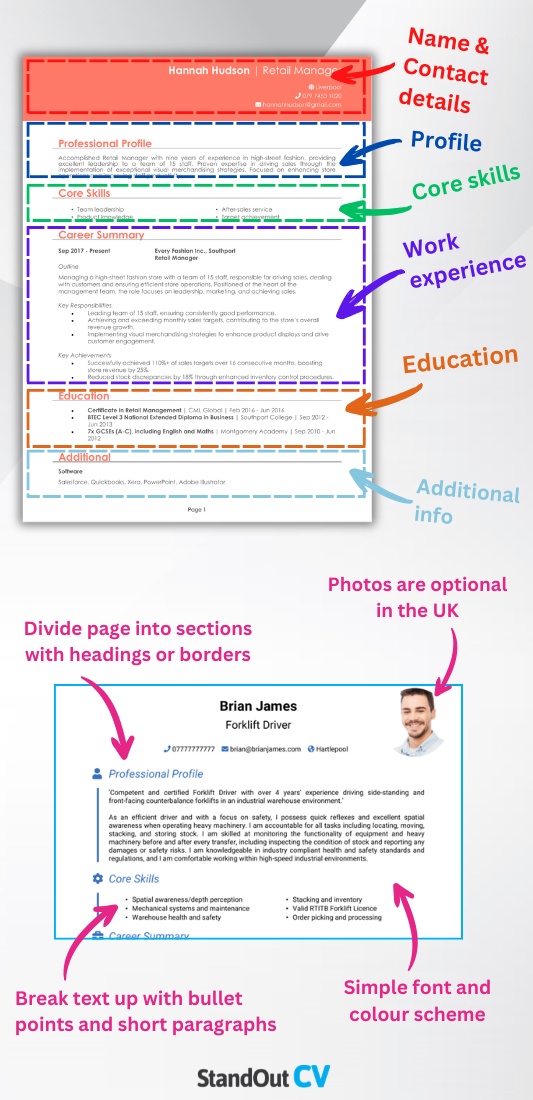
When it comes to aerospace, clarity and control are key – and your CV should follow the same principle. Recruiters and hiring managers need to identify your experience, qualifications, and technical specialisms without hunting through an unstructured layout or dense paragraphs.
Here’s the structure to follow:
- Name and contact details – Ensure your name and personal details are easily visible at the top. A photo is optional and depends on the role.
- Profile – Craft a short introduction that showcases your professional background and key accomplishments.
- Core skills – Provide a quick overview of your top skills that show why you’re a great fit.
- Work experience – Outline your career progression in reverse order, emphasising your contributions and successes.
- Education – Provide details on your academic background, including certifications or specialised training.
- Additional info – You can add hobbies or activities here that reflect your enthusiasm for the industry.
Use clearly labelled section headings, and break down text with bullet points so it’s skimmable. Keep your font professional, and avoid cramming too much in – a clean, breathable layout always wins. Aim to keep your CV length under two pages, using white space wisely to guide the reader’s eye. A coherent CV format communicates technical competence before they even read a word.
CV profile for Aerospace Engineering


Your CV profile is the first place to showcase your engineering strengths and the value you bring to a technical team. In a short, punchy paragraph, sum up what you do, what you specialise in, and how your work makes a difference.
Whether you’ve worked on design, testing, research, or production, this section should convey your professional identity – and the benefit you provide to any aerospace organisation.
Aerospace Engineering CV profile examples
Profile 1
Experienced Aerospace Engineer with over 10 years working in aircraft systems design and performance analysis for commercial aviation manufacturers. Skilled in CAD modelling, stress testing, and regulatory compliance. Proven track record in leading cross-functional engineering teams to deliver on safety and innovation targets.
Profile 2
Dedicated Aerospace Engineer with six years of experience in the defence sector, focusing on propulsion systems and thermal analysis. Strong background in simulations, component testing, and technical reporting. Experienced with MATLAB, ANSYS, and other industry-standard tools for design validation and optimisation.
Profile 3
Motivated Aerospace Engineering graduate with three years of hands-on experience in flight systems support and integration testing. Proficient in interpreting technical drawings, supporting maintenance teams, and documenting system performance. Passionate about continuous improvement and safe, efficient engineering solutions.
Details to put in your Aerospace Engineering CV profile
Include the following:
- Where you worked – Mention the kind of organisations you’ve worked for, from aerospace manufacturers to defence contractors or research institutions.
- Your top qualifications – Highlight your degree, accreditations, or certifications in aerospace or mechanical engineering.
- Essential skills – Refer to your core areas, like stress analysis, CAD modelling, FEA tools, or materials selection.
- Technical focus – Indicate whether your background is in structures, systems, propulsion, avionics, or R&D.
- Value delivered – Mention how your work improved performance, efficiency, safety, or innovation within a project or product lifecycle.
How should you write a core skills section?


This section gives a quick, high-impact summary of the hard CV skills you bring to the role – the ones that match what’s in the job spec. Focus on specific engineering software, analysis methods, and technical competencies.
Think less about soft skills and more about precision – recruiters want to see toolkits, technical knowledge, and project experience. CAD tools, MATLAB, thermal analysis, systems modelling, and regulatory knowledge are all fair game – just make sure it’s tailored to your specialism.
Key skills for an Aerospace Engineering CV
- Aerodynamic Analysis and Simulation – Applying principles of fluid dynamics to analyse airflow and optimise aircraft and spacecraft performance.
- CAD and 3D Modelling – Using software such as CATIA, SolidWorks, or Siemens NX to design detailed aerospace components and assemblies.
- Structural Analysis and Testing – Evaluating the strength, durability, and weight of materials and structures using tools like FEA (Finite Element Analysis).
- Propulsion System Design – Working on the design and integration of jet engines, rocket systems, and propulsion technologies.
- Flight Dynamics and Control – Modelling and analysing flight behaviour, stability, and control systems for various aerospace vehicles.
- Systems Integration and Avionics – Coordinating electrical, mechanical, and software systems to ensure proper function and compatibility.
- Materials Selection and Testing – Choosing and evaluating advanced materials like composites and alloys for performance under extreme conditions.
- CFD and Thermal Analysis – Using computational fluid dynamics and thermal simulation to assess heat transfer and environmental impact on design.
- Compliance with Aerospace Standards – Ensuring designs and processes meet regulatory requirements such as FAA, EASA, or MIL-STDs.
- Project Management and Collaboration – Working in multidisciplinary teams to deliver complex engineering projects on time and within budget.
Writing about your work experience


Here’s where you convert your technical skills into career evidence. Aerospace employers want to see how you’ve contributed to real-world projects, whether in design, testing, simulation, or manufacturing. Each job you list should clearly show your technical input and the measurable impact you had.
Whether you’re entry-level or highly experienced, this section is your launchpad. Start with your most recent work experience and work backwards. For each job, open with a short paragraph outlining your employer, your position, and the project or product area. Then use bullet points to break down responsibilities and achievements – highlighting the tools, processes, and outcomes involved.
Formatting your job history for your CV

- Outline – Describe the company or team you worked for, your role, and the type of projects you supported – e.g. commercial aircraft design, UAV development, or propulsion testing.
- Responsibilities – Use action words like “developed” and “analysed.” For example: “developed structural components using CATIA V5” or “analysed fluid dynamics in high-speed inlets using CFD tools.”
- Achievements – Highlight real-world results: improved fuel efficiency, reduced weight, shortened development cycles, or compliance with safety standards. Always quantify where possible.
Work experience samples for Aerospace Engineering
Aerospace Engineering | Veltrix Aviation Technologies
Outline
Worked on fixed-wing aircraft design and system integration for a global aerospace manufacturing company, contributing to new model development.
Responsibilities
- Conducted design calculations and supported 3D modelling using CATIA and SolidWorks
- Prepared documentation for system specifications, load analysis, and FEA simulations
- Collaborated with avionics and structural teams to ensure interface compatibility
- Participated in flight testing and supported troubleshooting activities
- Monitored compliance with EASA certification and internal QA processes
Achievements
- Improved design efficiency by 18% by automating routine simulation workflows
- Supported successful delivery of aircraft design package six weeks ahead of schedule
- Contributed to weight reduction initiative, saving 32kg per aircraft
Aerospace Engineering | Orbin AeroDefence Ltd
Outline
Supported propulsion systems analysis and thermal performance modelling for military-grade drones within a government contractor programme.
Responsibilities
- Developed and tested propulsion component models using MATLAB and Simulink
- Performed thermal stress assessments under extreme operational conditions
- Worked with procurement and supply chain teams to ensure component quality
- Prepared technical reports and presented findings to project leads
- Assisted with prototype evaluations and bench testing procedures
Achievements
- Enhanced engine cooling performance by 15% through design refinement
- Reduced testing cycle times by 20% with improved data logging setup
- Awarded internal recognition for accuracy in critical failure analysis
Aerospace Engineering | Novex Flight Systems
Outline
Provided support for aircraft maintenance and upgrade programmes at a specialist flight systems engineering consultancy.
Responsibilities
- Assisted in integration and testing of avionic upgrades on legacy aircraft
- Created and updated wiring diagrams and technical drawings
- Performed system diagnostics during ground testing and flight-readiness checks
- Documented engineering change requests and reviewed implementation impact
- Maintained strong liaison with MRO teams during modification work
Achievements
- Helped reduce ground downtime by 30% during a multi-aircraft upgrade programme
- Improved fault tracing efficiency with redesigned system flow diagrams
- Received commendation from senior engineers for attention to detail during testing
How to write your education section


Aerospace roles require heavy levels of academic training and education, so this section should be clear and well-structured. Include your degree title, awarding university, and dates. If relevant, add special modules, your thesis title, or key projects – especially if you’re early in your career or the experience was highly technical.
If you’ve done postgraduate study, relevant certifications, or CPD, include those too.
Recommended qualifications for Aerospace Engineering
- BEng/MEng in Aerospace Engineering – Core qualification for most aerospace roles
- MSc in Aerospace Systems or Avionics – Strong for those specialising in high-tech or R&D fields
- Chartered Engineer (CEng) – A recognised mark of professionalism and seniority in engineering
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA) Training – Useful for simulation and structural integrity roles
- EASA Part 66 Licence (if applicable) – Key for those moving toward aircraft maintenance or airworthiness certification





